W3C "From Web information sharing to data attestation…automated authentication expected to save billions of dollars"
Summary
- The verifiable credentials (VC) technology developed by W3C is said to increase the reliability of global trade and digital identity systems, and is expected to result in billions of dollars in cost savings.
- VC-based systems emphasize that through selective disclosure of information they can protect companies' intellectual property and confidential information, and maintain trust in transactions.
- VC 2.0 has the technical foundation for large-scale use and is expected to develop into an API that directly connects browsers and digital wallets.
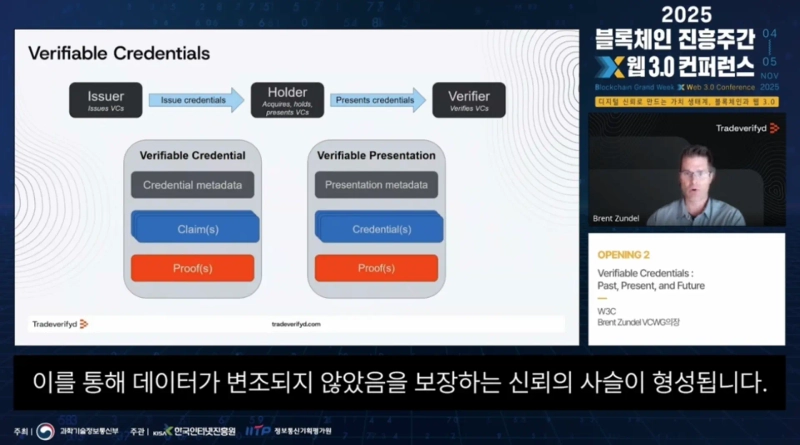
"The 'verifiable credentials (Verifiable Credentials·VC)' developed by W3C are not simply a technology to verify identity, but a technology that is changing how global trade and digital identity systems operate. In transaction processes such as trade, they can increase trust and, by selectively sharing only the necessary information, protect personal data while reducing costs by billions of dollars."
In the keynote speech at the "2025 Blockchain Promotion Week X Web 3.0 Conference" held on the 4th at COEX in Gangnam, Seoul, Brent Zundel, chair of the W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) Verifiable Credentials Working Group (Verifiable Credentials Working Group·VCWG), said this.
The W3C is an international standards organization founded under the leadership of Tim Berners-Lee, who created the World Wide Web (WWW), and has defined fundamental web specifications such as HTML and HTTP. The working group led by Zundel recently adopted the 'Verifiable Credentials Data Model 2.0' as an official standard. This standard was completed after nearly ten years of development and is beginning to be used across various industries. Observers say the web is evolving beyond a mere space for information to a stage that handles trust.
The concept of 'verifiable credentials' can be easily understood by the digital vaccine certificates used during the COVID-19 period. At that time, the structure that proved an individual's vaccination history without forgery or alteration and could be presented only when necessary is precisely the basic principle of VC. Issuers correspond to governments or medical institutions, holders to individuals, and verifiers to airlines or public agencies. In this way, information is securely issued and presented and verified only within the necessary scope, which is the core structure of VC.
He said, "The core of verifiable credentials is the 'selective disclosure' of information," adding, "Only the necessary information can be shared, protecting companies' intellectual property and confidential information. It can maintain trust in transactions." He added, "The traditional method of exchanging trade documents by email or invoice took a lot of time and cost, but VC-based systems automate issuance and verification, so billions of dollars in savings are expected."
Meanwhile, VC 2.0 also has the technical foundation for large-scale use. It uses a web-standard format called JSON-LD to easily connect with most internet systems, and through cryptographic signatures and status-checking functions it can automatically verify the issuance time and validity. Zundel said, "This standard will develop into an API that directly connects browsers and digital wallets (virtual asset wallets)," and "This will usher in an era in which governments, companies, and international organizations build trust infrastructure together," he predicted.

Minseung Kang
minriver@bloomingbit.ioBlockchain journalist | Writer of Trade Now & Altcoin Now, must-read content for investors.![[Today’s Key Economic & Crypto Calendar] US January Manufacturing PMI, etc.](https://media.bloomingbit.io/static/news/brief_en.webp?w=250)
![[Market] Bitcoin breaks below $76,000 as selloff shows no sign of easing](https://media.bloomingbit.io/PROD/news/0b328b54-f0e6-48fd-aeb0-687b3adede85.webp?w=250)
![[Market] Bitcoin slips below $77,000…Ethereum also breaks below $2,300](https://media.bloomingbit.io/PROD/news/f368fdee-cfea-4682-a5a1-926caa66b807.webp?w=250)

